Clinical Speckle Imaging
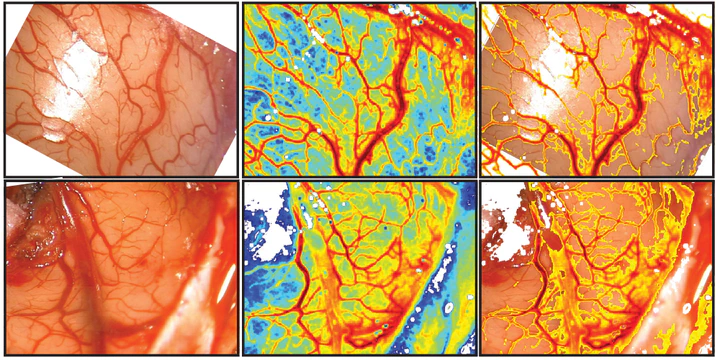 Intraoperative LSCI (Richards, 2014)
Intraoperative LSCI (Richards, 2014)Monitoring cerebral blood flow (CBF) during neurosurgery can provide important physiological information during a variety of highly-invasive procedures. These measurements could be useful for assessing whether blood flow has returned to presurgical baseline levels or for determining postsurgical tissue viability. Laser speckle contrast imaging (LSCI) has been used extensively for quantitative CBF imaging during preclinical research with animal models.
We are working to develop translational LSCI systems for real-time clinical applications during neurovascular procedures such aneurysm clippings or tumor resections. Our current designs adapt onto commercial neurosurgical microscopes (Fig. 1) and allow for continuous CBF imaging without disrupting normal use.
).](/project/clinical-speckle-imaging/schematic_huff6056a3550821702e69af9d2f98fcfc_280500_7dc6edc5d6edf2d364d590a7228fef93.webp)